Speed is the lifeblood of a website. Studies have shown that slow loading websites are the bane of Internet users and 47% of them expect a site to load in less than two seconds. 40% of people who wait more than 3 seconds will likely abandon a website.
I am sure that many of you would have sought out ways of tweaking your site to squeeze just that extra bit of performance out of it, but did you know that one of the most basic speed elements is the location of your server?
Although this is a very broad statement, today I will be walking through it with you and explaining how the location affects your website speed in different ways.
How Users Connect to Your Site?
When users type a URL into their browser address bars, a request is sent to your web server, which then sends your site data to the user. The request doesn’t take much time to travel to the server usually since there is not all that much data in it. However, if users are connecting to your site via a virtual private network (VPN), this can increase the request time as it first travels through VPN provider’s servers before reaching your website’s server. Luckily, this shouldn’t be a big problem if the user uses a high-speed VPN service, such as NordVPN.
However, the data that makes up your website is usually a lot bulkier and that takes time to travel back to the user to be displayed on their browser. The route that data travels through is usually mandated by information superhighways made up of massive data cables that traverse the globe.
Data is routed around the globe by a system of information superhighways in the form of submarine cables.
These are called submarine data cables and are how data is routed around the globe. Anything going from point A to Point B must follow these lines, with possible stops in between depending on route. The longer the distance the data must travel, the longer your site will take to load on the user’s browser.
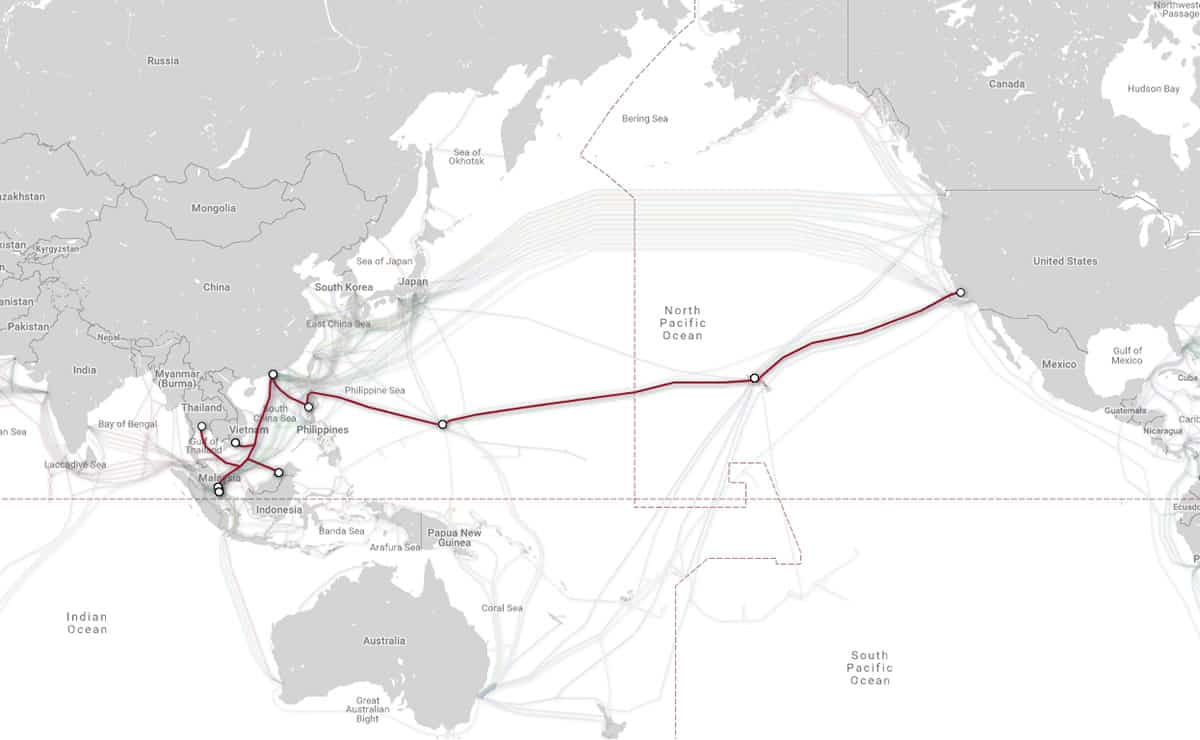
The AAG route from the USA to Malaysia isn’t a direct trip
Take for example a website hosted in Malaysia with a user trying to access it from the East Coast of the US. The data will most likely be routed via the Asia-America Gateway (AAG) Cable System, which links the US East Coast via California to Asia. Unfortunately, the distance is not only long but there are also routing stops along the way.
Choosing the Right Location to Host From
So, what does this distance/speed relationship have to do with your website? Most websites target visitors from specific regions or zones of the world (although there are some sites which do not necessarily have this focus). By being able to define your target audience, you can keep the distance between your users and the location your website is hosted at to a minimum.
Again, if we use the example of a site which targets US-based traffic, hosting that site directly on the US mainland would be highly beneficial. Alternatively, if you are targeting Asia-based traffic, then Singapore would be an ideal location since it is a major routing stop in Asia along the information superhighway system.
Once you’ve identified the target region of your desired traffic, check the web hosts you are interested in and see if they have any data centers close to that region. Many good web hosting service providers have multiple data center locations precisely for this reason.
One good example of a web host with multiple server locations is Hostinger. They show a keen awareness of the need for server proximity and have covered three major zones around the globe – the US, Asia, and Europe. If you sign up with them, choose the server location closest to your target market and you will be fine.
As of writing this article, the price of Hostinger’s shared hosting plans ranges from $0.80 – $3.45 per month. You can find out more about Hostinger by reading this Hostinger review.
Your Site Speed is Important
Google has indicated that speed is one of the metrics it uses to help rank web pages, but temper this with a touch of salt since it also realizes many sites make use of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). However, since the search engine has begun placing increased focus on the speed of loading on mobile devices as well, speed is still in the spotlight.
Here are some statistics which strongly indicate how important site speed is;
- Amazon found every 100ms of latency cost them 1% in sales
- Akamai research found a one-second delay results in 7% loss in conversions
- The same study showed a two-second delay increased bounce rates by 103%
- 79% of online shoppers won’t return to slow sites
Google is seeking a faster, more efficient web and rewards sites that meet these criteria. If you already have a site and would like to know how it performs, I recommend using WebPageTest. This useful tool lets you test the performance of your site from various locations around the world. Use that to gauge if your current host is suitable for your target market.
If you’re pressed for time, another useful tool you can try instead is the BitCatcha speed test which will perform tests from a set of multiple locations at the same time for you.
To round off this section, I’d like to share another interesting titbit of information: “Google will reduce the amount of crawlers it sends to your site if your server is slower than two seconds.” This means that new posts on your site will take longer to appear in search rankings, causing you to possibly lose out to competitors.
Conclusion
Having reached this point by now, there are several takeaways I hope you’ll get from this article. The first is that where your website is physically hosted is important relative to where your target audience is.
The second is that data travels along superhighway corridors and hosting in some major locations is better than others. there are also web hosts such as Hostinger which offer multiple server locations at key areas on the superhighway map so that you can host with them with a peace of mind.
Finally, your site speed is important since it affects not just how Google ranks your content, but also how users perceive your site. Do you really want to be known as ‘that slow-assed site’ just because you’re hosted in the wrong location?








